Keratoconus: Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
Keratoconus
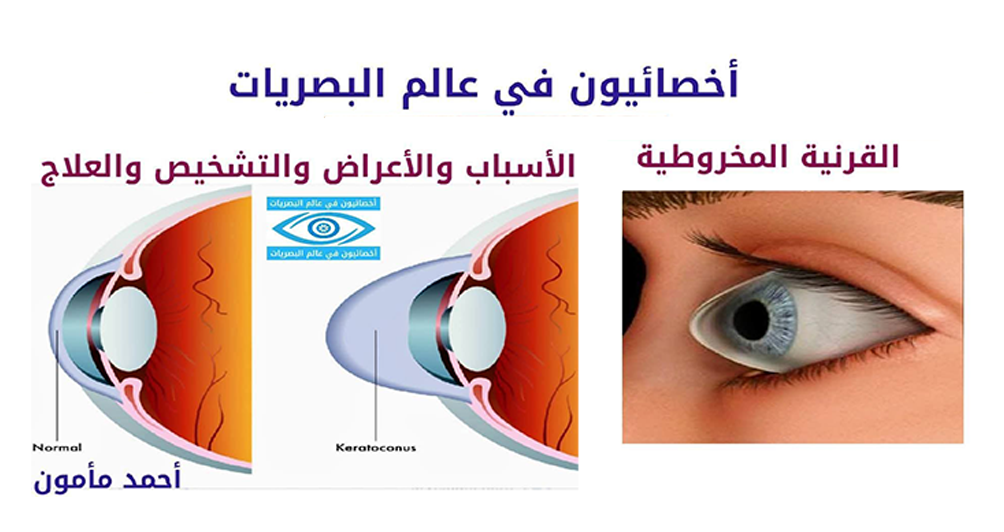
What is Keratoconus?
The cornea is a circular dome-shaped structure that covers the front of the eye. Keratoconus can be affected by diseases such as keratoconus, which occurs when the tissues that make up the cornea are damaged, causing it to change shape and become conical. Blurred vision is one of the most prominent symptoms of this condition. This condition is detected through an eye exam. Doctors treat keratoconus with contact lenses or surgery. A healthy diet also helps maintain corneal health.
Symptoms of Keratoconus
If someone with keratoconus feels their vision is rapidly deteriorating, they should see a doctor immediately. Keratoconus can also cause a number of symptoms, which worsen as the condition progresses.
These symptoms include:
– Blurred vision.
– Increased sensitivity to bright light.
– Frequently changing eyeglasses.
– Inability to see, which can occur suddenly. Causes of Keratoconus:
Keratoconus is a common disease that occurs in adolescence. It can occur in childhood and up to the age of 30, but it is rare for the disease to occur after the age of 40. The change in the shape of the cornea can occur quickly or over many years. This change can cause blurred vision, nighttime hallucinations, or an inability to distinguish lights. One or both eyes may be affected by this disease, but most often one eye is affected first, followed by the other. Protein fibers in the eye, called collagen, help hold the cornea in place. However, when these fibers become weak, they are unable to stabilize the cornea, and the cornea becomes conical. A decrease in antioxidants in the eye leads to weakening of the collagen fibers, leading to keratoconus. Keratoconus may also be caused by genetics. If one parent has the disease, it may be passed on to their children through genetics. It may also be caused by eye allergies, which can lead to eye rubbing, which can cause the cornea to change its shape to a conical shape. It is worth noting that a person with this disease may have a conical shape. Severe keratoconus may cause large scars to form on the back of the cornea.
Keratoconus Diagnosis:
To diagnose keratoconus, the doctor will ask the patient about their medical and family history. They will also perform a physical examination and an eye exam. They may also perform several other tests to diagnose the condition. These tests include:
-Reflexology: In this test, the ophthalmologist uses special equipment to measure vision to detect any vision problems. The doctor may also ask the patient to look through a special device containing different lenses to examine the structure of the eye. The doctor may also use a retinoscope to examine their vision.
-Light examination: During this test, the doctor will shine a light on the eye and then use a microscope to examine it. This will determine the shape of the cornea and detect any other eye problems. In some cases, the doctor may perform this test after giving the patient dilated eye drops to view the back of the eye.
Corneal examination: During this test, the specialist will shine a light directly onto the cornea to measure the reflection and determine the shape of the cornea.
Computerized keratotomy: The doctor will use a tomography scan to take pictures of the cornea and the surface of the eye. This test also helps measure the thickness of the eye.
Treatment of keratoconus:
Treatment of keratoconus depends on the severity of the condition and the progression of the disease. In mild cases, the disease may be treated with glasses, and the cornea will return to its normal shape within several years. However, if the cornea ruptures or if treatment with glasses fails, the doctor will treat keratoconus with one of the following treatments:
Treatment with contact lenses: The doctor may use various types of contact lenses to treat keratoconus. These types include:
Soft contact lenses: These lenses are used to treat mild cases to improve blurred vision.
Hard contact lenses: These lenses are used after soft contact lenses to provide clear vision. However, these lenses are uncomfortable for many people.
Piggyback lenses: If hard lenses are uncomfortable, your doctor will recommend attaching hard lenses over soft lenses.
Hybrid lenses: These lenses are hard in the center and soft at the edges. They are used for people who feel uncomfortable wearing hard lenses.
Scleral lenses: These lenses are used to treat severe cases of keratoconus. These lenses are fitted by an ophthalmologist, who will perform several tests before and during their fitting.
Surgery: A patient will require surgery if the cornea becomes scarred, becomes extremely thin, or suffers from severe vision loss. There are several surgical procedures that can be performed, including:
Corneal reshaping (rings): The doctor will place crescent-shaped plastic pieces in the cornea to improve its shape and vision.
Corneal Transplant: If the cornea becomes scarred or thin, the doctor will perform surgery to implant a new cornea into the eye. The doctor may also transplant part of the cornea or other tissue into the eye. It’s worth noting that complications may occur after a corneal transplant, such as eye infection, blurred vision, or the inability to wear contact lenses.
*Future Treatments: In the future, doctors may use ultraviolet rays and eye drops to strengthen eye tissue and collagen fibers, thus treating keratoconus.
Prevention of Keratoconus:
A person can protect themselves from keratoconus by avoiding exposure to dry air or smoke or wearing protective eyewear when exposed to them. Taking short breaks while working on the computer for long periods also helps prevent this disease. Avoiding dry eyes also helps prevent many eye diseases.
#Specialists_in_the_World_of_Optics
#Keratoconus




Leave a comment